Instantaneous and Average Power
Instantaneous power is a power that absorb by a sigle element. It is also a value of power p at time t is equal to instantaneous voltage at time t times the instantaneous current at time t.
formula:
p(t) = v(t) i(t)
each instantaneous voltage and current has its own formula:
v(t) = Vm cos(ωt + θ)
i(t) = Im cos(ωt + θ)
The Vm and the Im are the amplitudes or the peak values, and θv and θi are the phase angle of the element.
So we arrive this formula:
p(t) = v(t) i(t) = Vm Im cos (ωt + θv) cos (ωt + θi)
We apply the trigonometric identity.
cos A cos B = 1/2 [cos (A - B) + cos (A + B)]
and express Equation as:
p(t) = 1/2 Vm Im cos(θv - θi) + 1/2 Vm Im cos (2ωt + θv + θi)
average power is the average power of an instantaneous power in a period.
formula given is:
P = 1/T ∫ p(t) dt
by substituting p(t) in the equation:
P = 1/T ∫ 1/2 Vm Im cos(θv - θi) dt + 1/T ∫ 1/2 Vm Im cos(2ωt + θv + θi)dt
P = 1/2 Vm Im cos(θv - θi) 1/T ∫ dt + 1/2 Vm Im 1/T ∫ cos(2ωt + θv + θi) dt
The first integrand is constant and the average of the constant is the same. the second integrand is a sinusoid. The average of the sinusoid is over its period is 0 because the area under the sinusoid during a positive half cycle is canceled by the area under it during the following half cycle. th second tern will be vanished and the power becomes:
P = 1/2 Vm Im cos(θv - θi)
Example:
A current I = 10∠30 A flows through an impedance Z = 20∠ -22 Ω find the average power delivered to the impedance.
First we get the voltage across the impedance Z so we can solve the power delivered to the impedance.
V = IZ = (10∠30 A)(20∠ -22 Ω) = 200∠ 8 V
since we have the required voltage so:
P = 1/2 Vm Im cos(θv - θi)
P = 1/2 (200)(10) cos(8 - 30)
P = 1000 cos(8 - 30)
P = 927.18 W
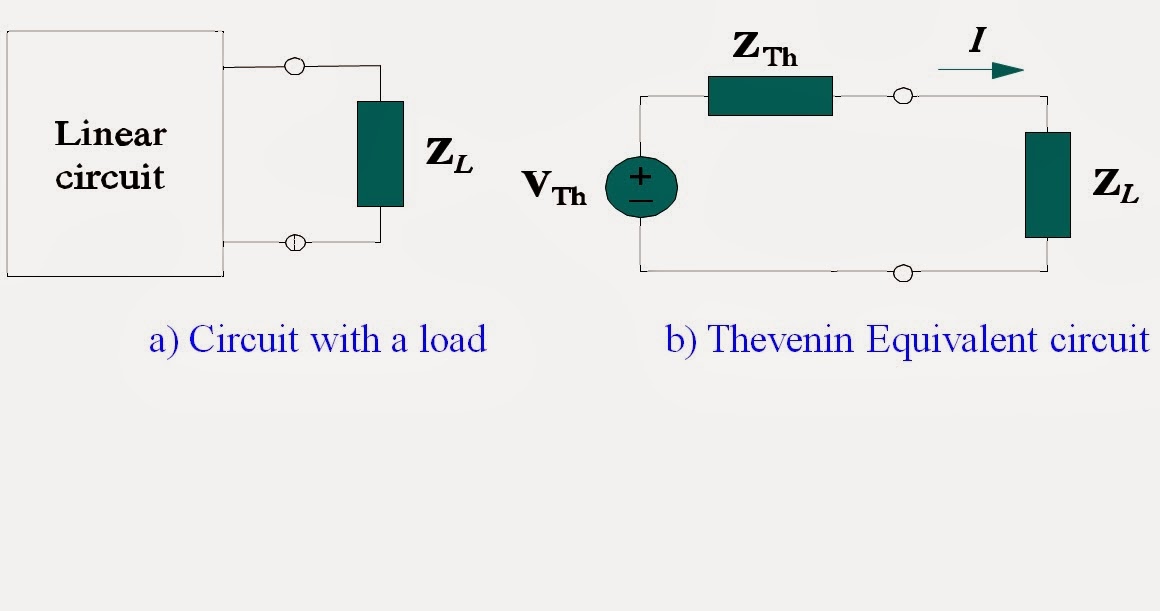
Maximum Average Power Transform
The maximum power transfer theorem states that, to obtain maximum external power from a source with a finite internal resistance, the load impedance must equal to the complex conjugate of the thevenins impedance.
Finding the maximum average power which can be transferred from a linear circuit to a Load connected.
Load ZL represents
any element that is absorbing the power generated by the circuit.
In rectangular form, the thevenin impedance ZTh and the load impedance ZL are:
Ajust RL and XL to get maximum P
Maximum Average Power Transform
The maximum power transfer theorem states that, to obtain maximum external power from a source with a finite internal resistance, the load impedance must equal to the complex conjugate of the thevenins impedance.
Finding the maximum average power which can be transferred from a linear circuit to a Load connected.
In rectangular form, the thevenin impedance ZTh and the load impedance ZL are:
Ajust RL and XL to get maximum P
Therefore:
ZL = RTh - XTh = ZTh will generate the maximum power transfer.
Maximum
power is:
For Maximum average power transfer to a load impedance ZL we must choose ZL as the complex
conjugate of the Thevenin impedance ZTh.





No comments:
Post a Comment